Understanding Electric Bike Fuse Types and Their Critical Role
Electric bicycle fuses serve as the safety guardians of your e-bike's electrical system, protecting expensive components from damage caused by overcurrent conditions and short circuits.
When excessive current flows through the system, the fuse acts as a sacrificial device, melting its internal element to break the circuit and prevent catastrophic damage to the battery, motor, and controller.
This comprehensive guide explores the various fuse types available for electric bicycles and their specific applications.
Primary Fuse Categories Used in Electric Bicycles
Blade Fuses: The Modern Standard
Blade fuses represent the most prevalent type found in contemporary electric bicycles.
These fuses feature a flat, rectangular plastic body with two metal prongs that plug directly into a socket, making them easily recognizable and simple to replace.
The automotive-style design has been widely adopted in the e-bike industry due to their reliability and availability.
Blade fuses come in three primary sizes:
-
Mini blade fuses (2A-30A): Ideal for lighting circuits and low-power accessories
-
Standard blade fuses (5A-40A): Perfect for battery protection and controller input circuits
-
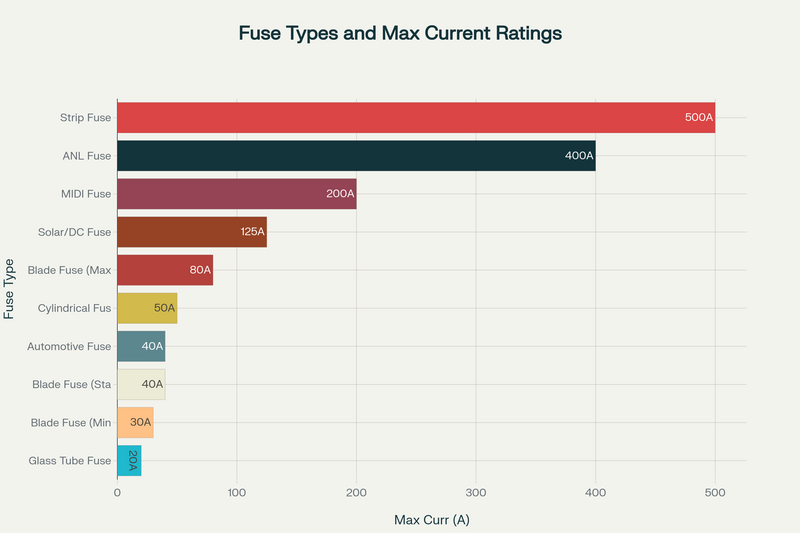
Maxi blade fuses (20A-80A): Designed for high-power motor circuits and main system protection
The key advantage of blade fuses lies in their visual inspection capability. A blown fuse typically shows a broken metal element visible through the transparent plastic body, making diagnosis straightforward.
Glass Tube Fuses: Traditional Protection
Glass tube fuses represent the traditional approach to electrical protection in older e-bike models.
These cylindrical fuses feature a glass body with metal caps on both ends, containing the fusible element within. While less common in modern applications, they remain relevant for retrofit applications and charging circuits.
The primary disadvantage of glass tube fuses is their fragility and decreasing availability in the market. However, they offer cost-effectiveness and are suitable for lower current applications typically ranging from 1A to 20A.
ANL Fuses: High-Current Protection
ANL fuses provide high-current protection for demanding e-bike applications.
These bolt-down style fuses feature a clear window that allows for visual status indication and can handle currents ranging from 20A to 400A. The gold/nickel plated terminals offer corrosion resistance, making them suitable for harsh environmental conditions.
ANL fuses are particularly valuable for high-power e-bike systems operating at 48V to 80V with significant current demands. Their high interrupt capacity (up to 2,700 amps DC) makes them ideal for battery protection in systems prone to short circuit conditions.

Electric Bike Fuse Types and Their Maximum Current Ratings
Cylindrical Fuses: Versatile Protection
Cylindrical fuses offer versatile mounting options and are commonly used in general protection and charging circuits. These fuses feature a ceramic or plastic body and can accommodate current ratings from 3A to 50A across voltage ranges of 24V to 72V.
The blade fuse and cylindrical fuse designs both provide reliable protection, with the choice often depending on mounting requirements and space constraints within the e-bike's electrical system.
RELATED: Where is the fuse on an electric bike?
Specialized Fuse Applications
Circuit Breakers vs. Traditional Fuses
While traditional fuses require replacement after activation, circuit breakers offer resettable protection.
Circuit breakers provide several advantages including dead-front design for enhanced safety, both magnetic and thermal protection, and on/off switch functionality.
However, fuses maintain certain advantages including faster response times (less than one quarter cycle), lower initial cost, and smaller physical footprint.
The choice between fuses and circuit breakers often depends on user convenience requirements and maintenance accessibility.
Thermal Fuses: Temperature-Based Protection
Thermal fuses provide temperature-based protection by opening the circuit when a predetermined temperature is reached. These specialized fuses are particularly valuable in battery protection systems where thermal runaway poses a significant risk.
Thermal fuses can degrade over time, particularly when subjected to repeated thermal cycling or high current loads. Their operation depends on temperature thresholds rather than current levels, making them complementary to traditional overcurrent protection.
Fuse Sizing and Selection Guidelines
Voltage Rating Considerations
Proper voltage rating selection is crucial for safe operation. While some sources suggest that 32V automotive fuses can be used in 48V systems, electrical safety principles recommend matching or exceeding the system voltage.
DC-rated fuses specifically designed for electric vehicle applications offer superior arc suppression and safety margins.
Current Rating Selection
The amperage rating of a fuse should be selected based on the maximum continuous current the circuit will carry. A general rule suggests that maximum continuous current should not exceed approximately 68% of the fuse rating.
For a 1000W motor on a 48V system, this translates to approximately 21A continuous current, suggesting a 30A fuse would be appropriate.
Environmental Protection
Waterproof fuse holders provide IP67-rated protection against dust and moisture ingress. The sealed design is particularly important for e-bikes exposed to weather conditions and road spray. Heat shrink tubing can provide additional environmental protection for inline installations.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Installation Techniques
Fuse installation should follow specific safety protocols.
The fuse should be positioned as close to the battery as possible to provide maximum protection. Insulating gloves should be worn during installation, and the system should be completely de-energized before any work begins.
Testing and Diagnosis
Multimeter testing provides the most reliable method for fuse verification.
Set the multimeter to continuity mode and test across the fuse terminals. A good fuse will show zero resistance, while a blown fuse will display infinite resistance. Visual inspection alone is insufficient, as internal damage may not be visible.
Replacement Procedures
When replacing a blown fuse, always use the exact same amperage and voltage ratings.
Never substitute a higher-rated fuse, as this can compromise system protection and create safety hazards.
Repeatedly blowing fuses indicates an underlying electrical problem that requires investigation.
Common Fuse Locations in Electric Bicycles
Battery Compartment Integration
The most common fuse location is within the battery compartment, either integrated into the battery pack or positioned near the main power connection.
This placement provides optimal protection for the entire electrical system powered by the battery.
Controller Housing Protection
Some e-bikes feature fuse protection within the controller housing, safeguarding the power electronics against overcurrent conditions.
This secondary protection level helps prevent controller damage in case of motor faults or wiring issues.
External Fuse Box Systems
Premium e-bike models may incorporate dedicated external fuse boxes for easy maintenance access.
These systems typically feature multiple fuse protection for different circuits including lighting, motor power, and accessory circuits.
Troubleshooting Common Fuse Issues
Identifying Blown Fuse Symptoms
Blown fuse symptoms include sudden power loss, non-functioning electrical components, and inability to charge the battery.
The e-bike may start normally but shut down immediately under load, indicating insufficient current capacity or repeated fuse failure.
Addressing Repeated Fuse Failures
Repeated fuse failures typically indicate underlying electrical problems such as short circuits, damaged wiring, or component malfunctions.
Systematic troubleshooting should include visual inspection of wiring, continuity testing of components, and thermal inspection of connections.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular fuse inspection should be part of routine e-bike maintenance.
Check for corrosion on fuse terminals, loose connections, and signs of overheating. Waterproof protection should be verified to prevent moisture-related failures.
Advanced Fuse Technologies
Electronic Fuses (eFuses)
Electronic fuses represent the next generation of circuit protection technology.
These semiconductor-based devices offer resettable protection, programmable current thresholds, and faster response times compared to traditional fuses.
eFuses can restart millions of times without replacement, making them ideal for high-reliability applications.
Smart Fuse Systems
Smart fuse technologies incorporate monitoring capabilities and communication interfaces to provide real-time status information.
These systems can detect fault conditions, log events, and provide diagnostic information to enhance system reliability and maintenance efficiency.
Conclusion
Electric bicycle fuses represent a critical safety component that requires careful selection, proper installation, and regular maintenance.
Understanding the various fuse types, their applications, and sizing requirements enables e-bike owners to make informed decisions about their electrical system protection.
The evolution toward higher voltage systems and increased power demands continues to drive innovation in fuse technology, with electronic fuses and smart protection systems representing the future of e-bike safety.
Proper fuse maintenance and replacement procedures ensure reliable operation and protect valuable electrical components from damage.
By following the guidelines presented in this comprehensive guide, e-bike owners can ensure their electrical systems remain safe, reliable, and properly protected throughout their operational life.