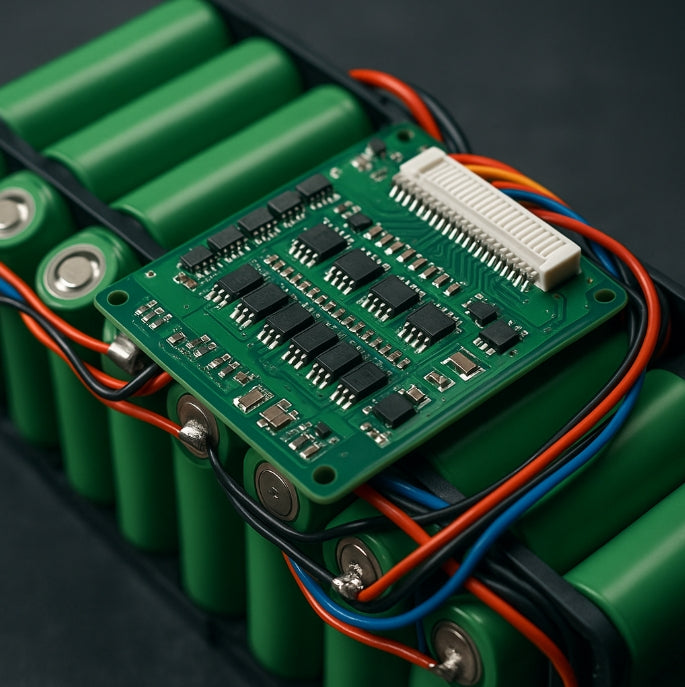
Overview
An electric bicycle battery management system (BMS) is the sophisticated electronic brain that monitors, controls, and protects your e-bike's battery pack.
This critical component ensures safe operation, maximizes battery life, and prevents dangerous conditions that could lead to overheating, fire, or battery damage.
Modern BMS technology serves as the invisible guardian between your battery cells and the outside world, making e-bikes safer and more reliable than ever before.
What Is a Battery Management System
The Core Function of BMS in E-Bikes

A battery management system is an intelligent electronic circuit that continuously monitors individual battery cells within your e-bike's battery pack.
Unlike a simple on/off switch, a BMS performs complex calculations and real-time monitoring to ensure each cell operates within safe parameters.
The system tracks voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge across all cells simultaneously.
Modern e-bike batteries typically consist of multiple lithium-ion cells connected in series to achieve the desired voltage (36V, 48V, or higher).
Without proper management, these cells can become imbalanced, leading to reduced performance, shortened lifespan, or safety hazards. The BMS prevents these issues by acting as a sophisticated traffic controller for electrical energy.
Critical Safety Functions
The BMS safety features include multiple layers of protection against common battery hazards:
-
Overcharge Protection: Prevents individual cells from exceeding their maximum voltage (typically 4.2V for lithium-ion cells), which could cause overheating or fire
-
Over-discharge Protection: Stops discharge when cells reach minimum voltage levels, preventing permanent damage
-
Thermal Management: Monitors temperature and can reduce current flow or shut down the system if dangerous temperatures are detected
-
Short Circuit Protection: Immediately cuts power if a short circuit is detected, preventing catastrophic failure
-
Current Limiting: Prevents excessive current draw that could damage cells or create safety hazards
How BMS Technology Works
Cell Monitoring and Voltage Management
The BMS cell monitoring system uses precision sensors to measure the voltage of each individual cell or cell group in the battery pack.
Advanced BMS units can monitor voltages with accuracy of ±1.6mV, ensuring precise control over charging and discharging processes. This continuous monitoring allows the system to detect imbalances before they become problematic.
When charging, the BMS ensures that all cells reach full capacity simultaneously. During discharge, it prevents any single cell from being over-depleted, which could cause permanent damage.
The system accomplishes this through sophisticated algorithms that calculate optimal charging and discharging parameters in real-time.
Temperature Sensing and Thermal Protection

Temperature monitoring is crucial for e-bike safety, as lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to thermal conditions. The BMS incorporates multiple temperature sensors placed strategically throughout the battery pack to monitor hot spots and overall thermal conditions.
When temperatures exceed safe limits, the system can:
-
Reduce charging current to slow heat generation
-
Activate cooling systems if present
-
Completely shut down charging or discharging to prevent thermal runaway
-
Alert the rider through warning indicators
State of Charge (SOC) and State of Health (SOH) Calculations
Modern BMS algorithms use advanced mathematical models to accurately estimate how much energy remains in the battery and its overall health status. These calculations consider factors such as:
-
Current voltage under load
-
Historical charging and discharging patterns
-
Temperature effects on capacity
-
Age-related degradation
This information is communicated to the e-bike's display system, providing riders with accurate range estimates and battery health information.
Advanced BMS Features: Cell Balancing and Energy Management
Passive vs Active Cell Balancing

Cell balancing is one of the most important functions of a modern BMS, ensuring all cells in the battery pack maintain similar charge levels. There are two primary methods:
Passive Balancing: Uses resistors to dissipate excess energy from higher-charged cells as heat. This method is simpler and less expensive but wastes energy and generates heat. Passive balancing typically operates at currents between 0.1A to 1A and is most effective during charging.
Active Balancing: Transfers energy between cells using capacitors, inductors, or transformers. This method is more efficient as it redistributes rather than wastes energy, can operate during charging or discharging, and supports higher balancing currents up to 6A. Active balancing is particularly beneficial for high-capacity batteries and fast-charging applications.
Energy Efficiency and Range Optimization
A well-designed BMS can extend your e-bike's range by ensuring optimal energy utilization. The system accomplishes this through:
-
Intelligent load management that prevents unnecessary energy waste
-
Regenerative braking coordination that captures energy during braking
-
Efficiency optimization that adjusts power delivery based on riding conditions
-
Predictive algorithms that anticipate energy needs and adjust accordingly
Communication and Monitoring Capabilities
Modern BMS communication systems use various protocols to interface with other e-bike components and external devices:
CAN Bus: Provides robust, high-speed communication for real-time control applications
UART: Simple, low-power protocol suitable for basic monitoring applications
RS-485: Enables long-distance communication in distributed battery systems
Bluetooth/WiFi: Allows wireless monitoring through smartphone apps
BMS Installation and Maintenance: Ensuring Peak Performance
Professional Installation Guidelines
BMS installation requires careful attention to proper wiring, thermal management, and safety protocols. Key considerations include:
-
Proper connection of balance leads to ensure accurate cell monitoring
-
Secure mounting with adequate ventilation for heat dissipation
-
Correct configuration of charge and discharge circuits
-
Verification of all safety parameters before initial use
Routine Maintenance and Monitoring
Regular BMS maintenance helps ensure long-term reliability and safety:
Monthly Checks: Verify proper operation of charging system and check for any error codes or warnings
Quarterly Inspections: Examine physical connections, check for signs of overheating, and verify balance wire integrity
Annual Calibration: Perform full charge/discharge cycles to calibrate SOC algorithms and assess overall battery health
Software Updates: Keep BMS firmware updated to benefit from latest safety improvements and features
Testing and Troubleshooting
BMS testing can be performed using standard multimeter techniques:
-
Visual Inspection: Check for loose connections, damaged wires, or components
-
Voltage Testing: Measure individual cell voltages to identify imbalances
-
Temperature Verification: Ensure temperature sensors are providing accurate readings
-
Communication Testing: Verify proper data exchange between BMS and other components
When problems are identified, common solutions include BMS reset procedures, balance wire reconnection, or in severe cases, complete BMS replacement.
Safety Considerations and Best Practices
Preventing Common BMS Failures
BMS failure prevention requires understanding common failure modes and implementing preventive measures:
Overrating Issues: Ensure the BMS is properly rated for your battery's capacity and current requirements
Poor Design: Choose BMS units from reputable manufacturers with proper certifications
Environmental Factors: Protect the BMS from moisture, extreme temperatures, and physical damage
Maintenance Neglect: Follow recommended maintenance schedules and address issues promptly
Emergency Procedures and Safety Protocols
Understanding BMS emergency procedures is crucial for rider safety:
Know how to safely disconnect the battery in an emergency
Understand warning signs that indicate BMS problems
Have contact information for qualified technicians
Keep a fire extinguisher suitable for electrical fires nearby during charging
Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Modern e-bike BMS systems must comply with various safety standards:
-
UL certification for electrical safety
-
IEC standards for international compliance
-
CE marking for European market access
-
UN transportation standards for safe shipping
Future Developments and Emerging Technologies
Smart BMS and IoT Integration
The future of e-bike BMS technology includes enhanced connectivity and artificial intelligence features:
Cloud-based monitoring for fleet management and predictive maintenance
AI-powered algorithms that learn from usage patterns to optimize performance
Remote diagnostics that can identify problems before they become serious
Integration with smart city infrastructure for optimized charging and routing
Advanced Battery Chemistries
New battery technologies are driving evolution in BMS design:
Solid-state batteries requiring specialized monitoring protocols
Lithium-sulfur batteries with unique balancing requirements
Sodium-ion batteries offering improved safety characteristics
Advanced lithium-ion formulations with enhanced performance and safety
Conclusion: Your Path to E-Bike Battery Mastery
Understanding your e-bike's battery management system is essential for safe, efficient, and enjoyable riding. A properly functioning BMS protects your investment, ensures your safety, and maximizes your e-bike's performance.
By following the guidelines in this comprehensive guide, you'll be equipped to make informed decisions about BMS selection, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
The technology continues to evolve, with smarter, more efficient systems becoming available each year. Whether you're a casual commuter or an e-bike enthusiast, investing in quality BMS technology and proper maintenance will reward you with years of reliable, safe riding.
Remember that while this guide provides comprehensive information, complex BMS issues should always be handled by qualified technicians. Your safety and the longevity of your e-bike depend on proper installation, maintenance, and professional support when needed.